Wearable technology has become a transformative force in modern life, merging healthcare, fitness, and productivity into portable devices that can be worn daily. Gadgets such as smartwatches, fitness bands, and smart glasses track physical activity, sleep, heart rate, and other vital metrics. By delivering real-time insights, these wearables empower users to monitor health, set goals, and adopt healthier habits, ultimately enhancing overall wellness.
Beyond personal use, wearables are increasingly employed in professional environments. Devices can monitor employee movement, detect stress levels, and provide reminders for breaks or posture adjustments, helping organizations boost efficiency and well-being. In sectors like healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing, wearables improve safety by alerting workers to hazards or monitoring vitals during demanding tasks.
Wearable devices also support data-driven decisions. AI and analytics process collected information to deliver personalized advice, predictive insights, and actionable guidance. For instance, smart health devices can detect irregular heart patterns or sleep issues, notifying users or medical professionals promptly for preventive care. Productivity wearables analyze work patterns to optimize schedules, reduce fatigue, and increase focus.
The expansion of wearable technology has opened new opportunities for businesses and innovators. Companies developing devices, software, or health analytics platforms can tap into a growing market, generating revenue from device sales, subscriptions, and analytics services. As technology evolves, wearables will continue to enhance health, productivity, and quality of life.
Understanding Wearable Technology
Wearable technology encompasses electronic devices designed to be worn on the body, equipped with sensors and connectivity to collect and analyze data continuously. Unlike conventional gadgets, wearables offer constant interaction, providing insights into health, activity, or environmental conditions. Common examples include smartwatches, fitness trackers, smart glasses, wearable ECG monitors, and sensor-enabled clothing.
Core functionality relies on sensors and analytics to track metrics such as heart rate, sleep quality, calories burned, steps, posture, and stress levels. Advanced wearables leverage AI to generate recommendations, predictive alerts, and actionable insights for health and performance improvement.
Wearables are increasingly integrated into daily routines and workplaces. They assist individuals in tracking fitness, health, and wellness goals while helping professionals in monitoring safety, productivity, and fatigue in demanding work environments.
By facilitating data-driven insights and preventive measures, wearable technology empowers users and organizations to make informed decisions, optimize performance, and enhance safety, wellness, and efficiency.
Types of Wearable Devices
Smartwatches
Smartwatches combine traditional timekeeping with features like activity tracking, notifications, GPS, and app integration. They act as wearable extensions of smartphones for calls, messages, and productivity tools.
Example: Apple Watch, Samsung Galaxy Watch, Garmin
Benefit: Monitors health metrics, improves communication, and supports daily productivity.
Fitness Trackers
These devices track physical activity, sleep, heart rate, and calories burned. Integration with health apps helps users set goals and monitor progress over time.
Example: Fitbit Charge, Xiaomi Mi Band, Garmin Vivosmart
Benefit: Encourages regular exercise, healthier lifestyles, and consistent wellness tracking.
Smart Glasses
AR-enabled glasses overlay digital content on the real world, assisting in navigation, training, remote collaboration, or hands-free information access.
Example: Google Glass, Vuzix Blade, Microsoft HoloLens
Benefit: Enhances productivity, learning, and interactive experiences.
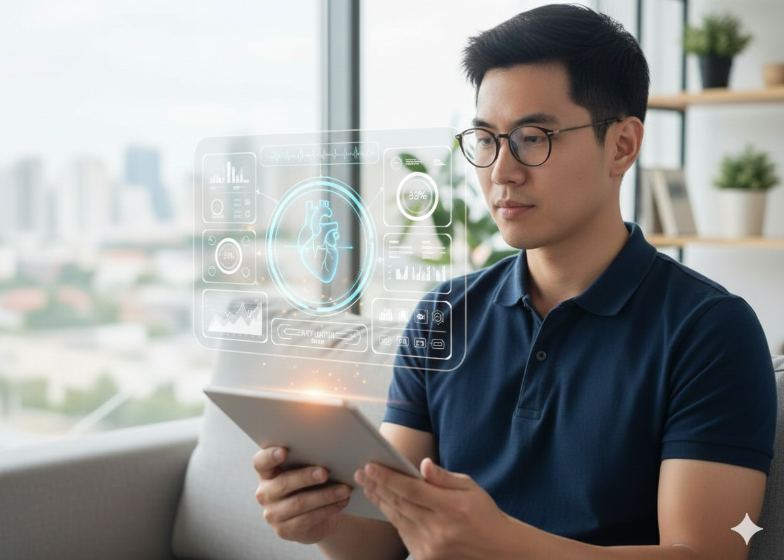
Wearable ECG and Health Monitors
Medical-grade devices monitor heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels, and ECG signals, allowing continuous health tracking for at-risk or chronic patients.
Example: Withings ScanWatch, AliveCor KardiaMobile
Benefit: Enables preventive healthcare and early detection of health anomalies.
Smart Clothing and Textiles
Embedded sensors in garments track heart rate, posture, body temperature, and movement, providing insights for sports, health, and workplace safety.
Example: Hexoskin Smart Shirt, Athos Performance Apparel
Benefit: Continuous monitoring without extra devices, supporting fitness and safety.
Wearable Audio Devices
Smart earbuds and hearing aids can track health metrics, deliver voice assistance, provide noise cancellation, and monitor vitals like heart rate or oxygen saturation.
Example: Apple AirPods Pro, Bose Hearphones
Benefit: Combines audio functionality with wellness and productivity tracking.
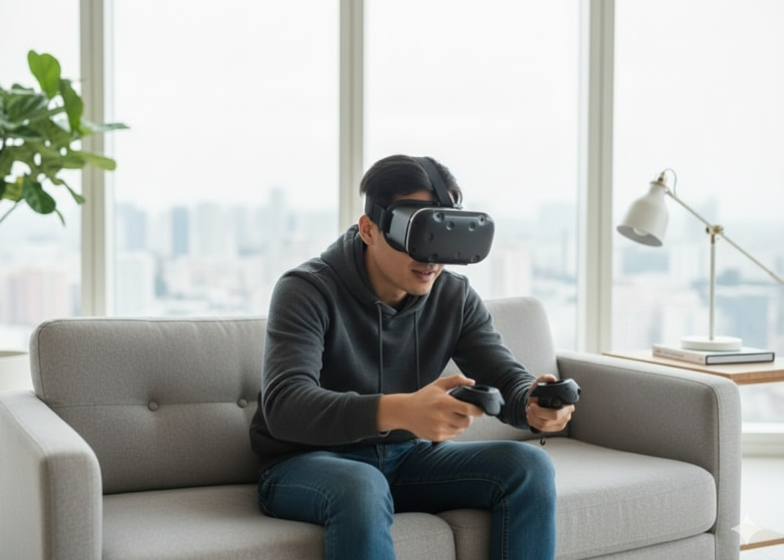
VR/AR Headsets
These immersive devices support gaming, training, education, and remote collaboration. Advanced models include motion tracking and eye-tracking for enhanced interactivity.
Example: Oculus Quest, HTC Vive, PlayStation VR
Benefit: Provides immersive experiences, interactive learning, and remote collaboration opportunities.
Challenges and Limitations
Device Costs
High prices of advanced wearables, including AR glasses and medical monitors, can limit adoption among average consumers and small businesses.
Data Privacy and Security
Wearables collect sensitive personal information. Poor security may expose health, location, and activity data to misuse.
Accuracy and Reliability
Sensor limitations or incorrect usage may lead to inaccurate readings, impacting health or productivity insights.
Battery Life and Maintenance
Frequent charging and maintenance are required for continuous tracking, which can affect convenience and consistent usage.
User Adoption and Learning Curve
Understanding how to use devices and interpret data may be challenging for non-tech-savvy users, resulting in underutilization.
Interoperability
Wearables must often sync with other devices or apps. Compatibility issues can reduce seamless operation and limit connected ecosystem benefits.
Over-Reliance on Technology
Dependence on wearables may reduce personal judgment and awareness, causing users to rely too heavily on devices for monitoring.
Data Overload
Large volumes of collected data may overwhelm users without proper analytics or interpretation, reducing actionable insights.
Summary
Wearable technology enhances health monitoring and productivity by providing continuous, actionable insights. Devices like smartwatches, fitness trackers, smart glasses, and medical monitors track vital signs, activity, and workplace metrics, enabling informed decisions for wellness and efficiency. While wearables improve convenience, personalization, and preventive care, challenges such as cost, data privacy, and compatibility exist. Despite these limitations, wearable technology continues to offer substantial opportunities for businesses, entrepreneurs, and professionals through sales, subscriptions, and health or productivity services.