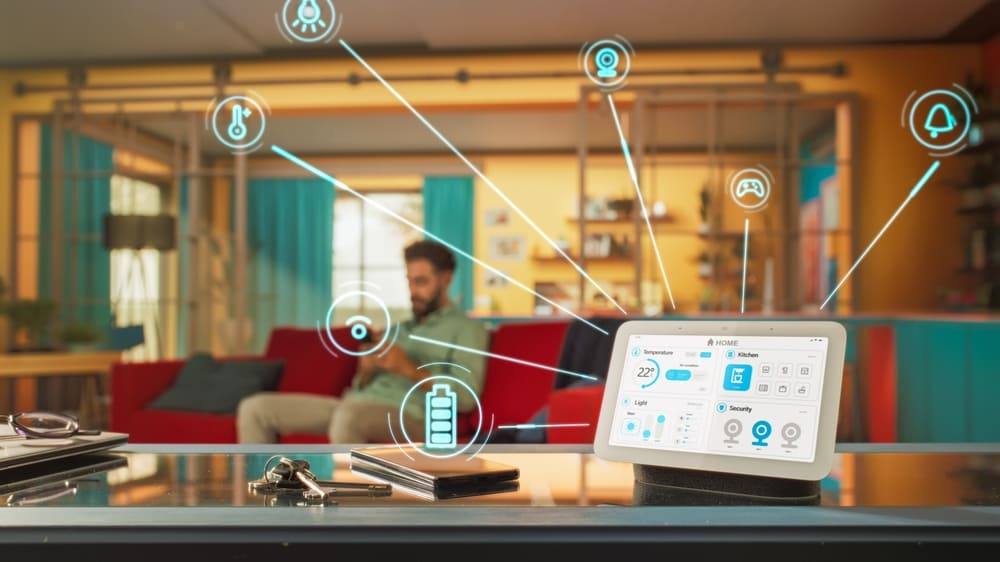
Smart homes and automation have reshaped modern living by integrating technology to enhance comfort, convenience, and safety. Early systems were limited to simple programmable timers for lights or heating. Today, advancements in IoT, sensors, and wireless networks allow devices to communicate, adapt to user preferences, and provide real-time automation for a truly connected home.
Modern smart homes feature a variety of interconnected devices, including smart lighting, thermostats, security systems, appliances, and entertainment setups. Voice assistants like Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri make control intuitive through voice commands, while AI-driven systems learn routines and optimize energy use, comfort, and convenience automatically.
Automation also significantly enhances home security. Smart locks, cameras, motion sensors, and alarm systems provide live alerts and remote monitoring. Mobile apps allow homeowners to manage their homes from anywhere, checking security, adjusting climate settings, or controlling devices with ease.
Additionally, smart technology boosts energy efficiency and reduces costs. Automated lighting, HVAC, and appliances cut unnecessary energy use, while AI systems analyze patterns to optimize consumption. As technology evolves, smart homes will continue to offer personalized experiences, convenience, and environmentally friendly living.
Key Components of a Smart Home
Smart Lighting Systems
Control brightness, color, and schedules remotely or automatically. Lights can adapt to time of day, occupancy, or natural light levels, creating customized environments for work, relaxation, or entertainment.
Example: Philips Hue, LIFX
Professionals installing smart lighting or selling devices can earn $40K–$100K/year, with small businesses generating $500–$2,000/month.
Smart Thermostats and Climate Control
Learn user habits and automatically adjust heating/cooling for comfort and efficiency. Integration with weather and energy rates further optimizes usage.
Example: Nest, Ecobee
Installation and consulting can generate $50K–$120K/year, while e-commerce sales may yield $1,000–$3,000/month.
Smart Security Systems
Cameras, sensors, smart locks, and video doorbells offer real-time alerts, remote monitoring, and AI-driven threat detection, improving safety and control.
Example: Ring, Arlo, August Lock
Installers and consultants can earn $50K–$130K/year, with DIY kits and monitoring services earning $500–$5,000/month.
Smart Entertainment Systems
Integrated smart TVs, speakers, and home theaters allow seamless control and personalized experiences through apps or voice commands.
Example: Sonos, Roku, Fire TV
Installers or content creators can earn $45K–$110K/year, with apps and services generating $1,000–$4,000/month.
Voice Assistants and Smart Hubs
Central devices manage all smart home components, enabling hands-free control over lighting, climate, security, and entertainment.
Example: Alexa, Google Assistant, Apple HomePod
Integration specialists can earn $50K–$120K/year, with skill/app development generating $500–$3,000/month.
Smart Appliances
Connected fridges, ovens, washers, and coffee makers allow remote control, automation, and energy optimization.
Example: Samsung Smart Fridge, LG Washer
Installation, repair, or sales can earn $40K–$100K/year, with additional revenue of $500–$2,500/month from services.
IoT Sensors
Detect motion, temperature, humidity, smoke, or leaks to automate responses and alert homeowners to issues in real-time.
Example: Aqara, Fibaro
Integration specialists earn $50K–$110K/year, with DIY kits and consulting earning $500–$2,000/month.
Home Automation Software and Apps
Centralized apps integrate devices, enabling routines, schedules, and remote management. Scenes like morning routines or vacation modes simplify control.
Example: SmartThings, HomeKit, Google Home
Developers and consultants earn $60K–$150K/year, with subscription-based apps generating $1,000–$5,000/month.
Benefits of Smart Homes and Automation
Convenience and Comfort
Automation and AI create effortless, personalized experiences, controlling lighting, climate, entertainment, and appliances remotely.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Smart devices optimize usage, reduce unnecessary consumption, lower utility bills, and support sustainable living.
Enhanced Security
Real-time monitoring, alerts, and remote control improve safety, prevent intrusions, and increase peace of mind.
Remote Access
Control and monitor smart devices from anywhere using apps or the internet, adding flexibility and convenience.
Personalized Experiences
AI-driven systems adapt to user habits, creating tailored lighting, temperature, entertainment, and lifestyle settings.
Integration and Interconnectivity
Devices communicate and trigger actions among each other, creating a seamless automated ecosystem.
Increased Property Value
Homes equipped with smart automation are more attractive to buyers, enhancing resale value and appeal.
Earning Opportunities
Smart home growth supports careers in installation, consulting, device development, and subscription services, earning $40K–$150K/year or $500–$5,000/month.
Challenges of Smart Homes and Automation
High Initial Costs
Advanced devices require significant investment, making full automation less accessible for some homeowners.
Complexity and Compatibility
Integrating devices from different brands can be challenging, requiring technical expertise to ensure seamless operation.
Privacy and Security Risks
Smart homes collect personal data. Weak security can lead to breaches or unauthorized access, raising privacy concerns.
Dependence on Internet and Technology
Reliable internet and cloud services are essential. Outages or technical failures can disrupt automation.
Maintenance and Updates
Regular updates and occasional maintenance are needed to keep devices secure and functional.
User Learning Curve
Not all homeowners are tech-savvy, so understanding and programming smart devices can be challenging.
Limited Standardization
Lack of universal standards can make adding or integrating new devices difficult, especially with proprietary systems.
Over-Reliance on Automation
Excessive dependence on automation can reduce engagement with basic tasks and cause difficulties during system failures.
Summary
Smart homes and automation have transformed traditional living spaces into intelligent, connected environments that provide convenience, security, energy savings, and personalized experiences. Devices such as lighting, thermostats, security systems, appliances, and voice assistants work together through IoT and automation platforms. While these innovations enhance comfort and lifestyle quality, challenges like cost, compatibility, and cybersecurity remain. As technology progresses, smart homes continue to improve daily living while opening opportunities for careers and businesses in installation, consulting, device development, and service offerings.